Address
1 Woodville Rd, Granville NSW 2142, Australia
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 9AM - 5PM
Weekend: Saturday - Sunday
Address
1 Woodville Rd, Granville NSW 2142, Australia
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 9AM - 5PM
Weekend: Saturday - Sunday
Electronic waste (e-waste) is one of the fastest-growing waste streams globally, creating significant environmental challenges. However, e-waste recycling plays a critical role in addressing these concerns by recovering valuable materials, reducing pollution, and ensuring sustainable disposal. In this article, we provide an in-depth look at the e-waste recycling process, outlining each step in a clear, SEO-optimized manner to help you understand how e-waste is effectively recycled and reused.
E-waste recycling refers to the process of recovering useful materials such as metals, plastics, and glass from electronic devices that have reached the end of their life cycle. By properly recycling electronics, we can minimize the environmental impact and conserve natural resources. Electronic items such as smartphones, computers, televisions, and batteries contain valuable components that can be repurposed.
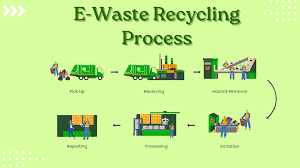
Recycling e-waste is a multi-step process that requires specialized equipment and techniques to safely recover and reuse materials. Here’s how the e-waste recycling process works:
The first step in the e-waste recycling process is the collection and transportation of discarded electronic devices. E-waste can be collected through various methods, including drop-off locations, curbside collection programs, and special collection events. After collection, the e-waste is transported to a certified recycling facility.
Upon arrival at the recycling center, e-waste is carefully sorted into categories based on its components and materials. This initial sorting process ensures that items are dismantled properly and that hazardous materials like mercury and lead are handled safely. Skilled technicians manually remove batteries, circuit boards, and other components that require specialized recycling methods.
The next phase of the e-waste recycling process involves mechanical processing, where larger machines shred e-waste into smaller pieces. These smaller parts are then further processed to separate metals, plastics, and other materials. This step typically involves techniques like crushing, grinding, and air classification, which help in the recovery of valuable materials.
After mechanical processing, the separated materials undergo further refinement. For metals like copper, aluminum, and gold, advanced techniques such as magnetic separation, eddy current separation, and flotation are used to separate metals from non-metallic materials. This step ensures that valuable metals are recovered without contamination.
In some cases, e-waste may undergo chemical or hydrometallurgical processing to recover precious metals like gold, silver, and platinum. These methods involve using water-based chemicals or heat to extract the metals from the shredded materials. Hydrometallurgical techniques are more environmentally friendly compared to traditional smelting methods, as they reduce harmful emissions.
Once precious metals have been extracted, the refining and purification process begins. This step ensures that the materials are free from impurities and are ready for reuse in the manufacturing of new electronics. The purified metals are often sold to manufacturers for the production of new devices.
Plastics and glass components are also recovered during the e-waste recycling process. Plastics are sorted, cleaned, and processed into pellets that can be used in the production of new plastic products. Glass is typically cleaned, crushed, and recycled to make new screens, windows, or even new electronic devices.
One of the most important aspects of the e-waste recycling process is the safe disposal of hazardous materials. Electronic devices often contain substances like lead, mercury, cadmium, and arsenic that can be harmful to both the environment and human health. Certified recycling facilities take special care to ensure these materials are disposed of according to environmental regulations and best practices.
Once all valuable materials have been recovered, they are sold to manufacturers for the production of new products. Recycled metals and plastics are used in the creation of new electronics, reducing the need for raw materials. This supports the concept of the circular economy, where products are reused, repaired, and recycled rather than disposed of.
The ultimate goal of the e-waste recycling process is to reduce the environmental impact of electronic waste. By recycling e-waste, we can conserve natural resources, reduce pollution, and prevent harmful chemicals from leaching into the environment. This process plays a vital role in reducing the carbon footprint of the electronics industry.
E-waste recycling is essential for several reasons:
The e-waste recycling process is constantly evolving with new technologies and methods that make it more efficient and environmentally friendly. With growing concerns over e-waste pollution, it’s more important than ever to ensure that electronics are properly recycled. As consumers, we have a responsibility to support responsible recycling initiatives and reduce our electronic waste footprint.
By understanding the steps involved in e-waste recycling, we can all contribute to a cleaner, more sustainable future. If you’re looking to recycle your old electronics, choose a certified e-waste recycling facility that follows proper procedures to ensure the safe recovery of materials.